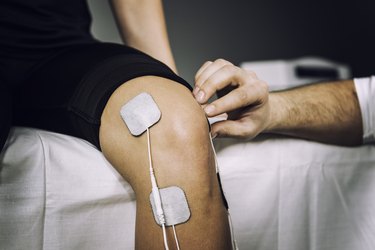
The prevalent abuse of anabolic steroids suggests that people have a strong interest in building muscle. Sports authorities have banned these performing-enhancing substances because of their inherent risk. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, TENS, and electrical myostimulation, EMS, give you many of the health benefits of anabolic steroids without their side effects.
Read more: What Are the Dangers of Injecting Steroids?
Video of the Day
Video of the Day
Use an Electric Muscle Stimulator
The use of electrical stimulation, electrotheraphy, has a fascinating history. In modern medicine, a TENS unit offers electrical stimulation without causing muscle contractions. This device contrasts with an EMS unit which causes muscle contractions.
The Benefits of EMS
Electrical stimulation offers you a popular, effective treatment. Most people use it as a pain remedy. A 2017 report in PLoS One showed that electrical stimulation gives knee arthritis patients the most cost-effective way to manage their pain. This low cost opens up many possibilities. You can, for example, use electrical stimulation to quickly and cheaply build muscle.
Electrical stimulation has other advantages as well. The units are easy to use, and treatment rarely causes side effects. Being non-pharmacological, there's no chance of electrical stimulation causing a drug interaction or an overdose. In most countries, you can buy your own unit and use it as much as you want. It's best, however, to have a health care expert create a unique protocol specifically designed for your needs.
Read more: Electrical Stimulation Therapy vs. Massage Therapy
The Parameters of EMS
An EMS unit sends pulses of electricity from a portable device to electrodes lying atop intact skin. People given EMS usually describe feeling a mild shock during treatment. That feeling makes it difficult for scientists to do a sham control or placebo treatment without the subjects noticing the difference. The mild shock forces your muscle cells to fire causing a contraction.
These devices have many settings, and those settings control the nature of the pulses. A 2016 paper in Clinical Review described the details of these parameters including frequency, duration and shape. Doctors usually prescribe either high-frequency EMS or low-frequency EMS. Clinicians consider high-frequency EMS the standard treatment because it usually gives the best results.
Read more: How to Use a TENS Unit to Tone Muscles
The Mechanisms of EMS
Using an EMS unit releases natural painkillers and activates the receptors for these endorphins. This change causes analgesia and decreases pain. Such effects explain why doctors often prescribe electrical stimulation for chronic pain.
The muscle-building effects of EMS work through an additional mechanism. The anabolic actions of EMS appear only near the electrode site. This finding suggests that immunomodulators and hormones don't play a major role. Instead, the muscle contractions triggered by an EMS unit appear critical.
Your body may not make much of a distinction between theses contractions and those caused by resistance exercise. Both interventions increase blood flow, muscle fatigue and metabolism. Most important, both treatments make patients more functional.
EMS in Younger Adults
Researchers have documented more than 3 million cases of anabolic steroid abuse in the United States. A 2017 report in the IOP Conference Series explored the potential of EMS to build muscle in the population most inclined to abuse steroids — younger men.
Participants did EMS four times a week for three months. Each session lasted about 30 minutes, focusing on the upper arm muscles. Compared to baseline, the subjects showed about a 4 percent increase in muscle size. However, the treatment did not increase muscle strength.
Read more: 6 Rules of Gaining Muscle Mass
EMS in Older Adults
Age-related muscle decay — sarcopenia — will eventually catch up with everyone. Institutionalization increases your risk of experiencing this medical condition. Doctors recommend doing physical activity to combat sarcopenia, but many barriers to exercise exist in older adults. A 2014 article in Experimental Gerontology looked at using EMS to overcome some of these barriers.
These researchers randomly assigned female and male nursing home residents to one of three conditions: exercise, EMS or exercise combined with EMS. Doing this protocol for four months led to an increase in muscle size in all three groups. However, only the combined treatment increased the clients' mobility.
Read more: Do Muscles Deteriorate Due to a Lack of Exercise?
EMS for SCI Patients
People with a spinal cord injury, SCI patients, often lose muscle strength. Eventually, this loss of muscle strength causes a loss of mass. Low-intensity EMS doesn't usually help recover these losses. A 2018 report in Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise looked at the impact of high-intensity EMS.
Patients did 12 weeks of rehabilitative EMS exercises. Compared to baseline, these knee extensions caused increases in muscle strength and muscle mass. They also improved the patients' cholesterol level and quality of life.
Read more: Acupuncture for Nerve Regeneration
EMS and COPD Patients
Many diseases cause muscle loss. Unfortunately, the treatments for many diseases also cause muscle loss. Leukemia patients, for example, have to manage the muscle loss caused by cancer and chemotherapy.
People with chronic obstructive pulmonary artery disease, COPD, also struggle with muscle loss, and EMS may help prevent this progressive decay. A study in Respiratory Medicine explored this possibility in COPD patients.
Researchers put patients into two groups: treatment and control. The treatment group did EMS five days a week for eight weeks. The patients did two 45-minute sessions on treatment days. Compared to the control group, the treatment group showed increases in muscle mass. They also performed better on the cycling tests done after completing the treatment.
This study also offers an insight into the mechanisms of EMS. Following treatment, the patients had higher levels of endorphin markers and lower levels of inflammation markers.
Read more: Diseases That Cause Muscle Wasting
EMS During Immobilization
Hospitalization triggers muscle loss irrespective of disease. In fact, any type of immobilization will rapidly break down the muscle tissue of healthy, younger adults within a few days. The authors of a study from Maastricht University sought an easy method to prevent this unwanted change.
The subjects had a leg immobilized with a cast-like device for five days. Half of the subjects received no treatment, and the other half received EMS treatment. The data showed that the control group lost 3.5 percent of their thigh mass and 9 percent of their thigh strength. The treatment group experienced no loss of mass and a 7 percent loss of strength.
Read more: Signs & Symptoms of Muscle Wasting
Knowing the Limits of EMS
You experience muscle fatigue after doing a hard workout, and EMS will cause a similar effect. Both medical patients and healthy adults experience this device-related fatigue.
Researchers have expended great effort to prevent this fatigue by varying the application parameters. Asynchronous stimulation decreases muscle fatigue in some EMS protocols, but these protocols often cause incomplete muscle contractions.
Decreasing the electrical intensity from the usual 20 Hz to 16 Hz in an asynchronous protocol prevents more ripple effects from happening, but they still occur more during EMS than during normal muscle contractions.
Read more: Side Effects of Overusing a TENS Machine
Knowing the Risks of EMS
Speak with a health care professional before using an electric muscle stimulator. Also, don't change the settings once you and your health care provider have agreed on them. Doctors consider EMS safe, but using a electrical stimulation can have unexpected consequences in some patients.
Contraindications also exist for EMS. For example, you shouldn't use a plug-in model near water. It's also wise to avoid using the unit while under the influence or during sleep. Pregnant people, heart patients and people with swelling should seek expert advice before doing EMS. Finally, you'll need to avoid certain electrode placements as some patterns can damage your body.
Read more: Contraindications for a TENS Machine
- PLoS One: Cost-Effectiveness of Adjunct Non-Pharmacological Interventions for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
- Clinical Review: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
- IOP Conference Series: Effect of Electrical Stimulation in Improving Muscle Tone (Clinical)
- Experimental Gerontology: Effects of Three Different Low-Intensity Exercise Interventions on Physical Performance, Muscle CSA and Activities of Daily Living
- Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise: Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation in People With Spinal Cord Injury
- Respiratory Medicine: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Improves Clinical and Physiological Function in COPD Patients
- Maastricht University: Interventional Strategies to Combat Muscle Disuse Atrophy